学习angr 我打算根据https://github.com/jakespringer/angr_ctf里的解题代码进行学习。
00_angr_find 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = ??? project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) initial_state = project.factory.entry_state() simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) print_good_address = ??? simulation.explore(find=print_good_address) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno())) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 创建Angr项目,angr会对二进制文件解析。
1 project = angr.Project(path_to_binary)
创建一个初始状态,通常从程序的入口点开始,即文件的入口函数main。
1 initial_state = project.factory.entry_state()
创建一个模拟管理器,通过这个模拟器可以使用很多工具,对二进制文件进行搜索和执行。
1 simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state)
自动探索路径,直到找到一个到达find参数指定的地址的状态。
1 simulation.explore(find=print_good_address)
这是一个列表,如果搜索成功,这个列表会包含所有可到达目标地址的状态。
从成功状态中,提取标准输入的内容。
1 2 solution_state = simulation.found[0] solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()).decode()
01_angr_avoid 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) initial_state = project.factory.entry_state( add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) print_good_address = 0x80485f7 will_not_succeed_address = 0x80485bf simulation.explore(find=print_good_address, avoid=will_not_succeed_address) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()).decode()) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 这次程序中不仅有成功路径,还有一些我们不希望进入的“陷阱”路径(例如,一个会打印失败信息然后退出的路径)。我们需要找到成功路径,同时避开这些陷阱。
在探索路径的时候,avoid参数可以避免某些状态的产生。比方说,不进入基本块A,则不会在基本块A处产生新状态,基本块A之后的基本块也不会继续通过基本块A产生新状态。
1 simulation.explore(find=find_address, avoid=avoid_address)
02_angr_find_condition 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) initial_state = project.factory.entry_state( add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()).decode()) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 有时候,可能不知道确切“成功”的指令地址,而是某种行为。比如说,某个基本块会标准输出“Good Job.”。
explore方法的find和avoid参数不仅可以接受地址,还可以接受一个函数。这个函数会以一个state对象为参数,返回True代表找到了或者应该避开,而返回False代表没找到成功状态或者不应该避开。
Angr会在每一步执行后,用这些函数评判当前状态,如果状态是True,就代表成功了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output
03_angr_symbolic_registers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 import claripy import sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) start_address = 0x80488c7 initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) password0_size_in_bits = 32 password0 = claripy.BVS('password0' , password0_size_in_bits) password1_size_in_bits = 32 password1 = claripy.BVS('password1' , password1_size_in_bits) password2_size_in_bits = 32 password2 = claripy.BVS('password2' , password2_size_in_bits) initial_state.regs.eax = password0 initial_state.regs.ebx = password1 initial_state.regs.edx = password2 simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval (password0) solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval (password1) solution2 = solution_state.solver.eval (password2) solution_string = ' ' .join(map ('{:x}' .format , [ solution0, solution1, solution2 ])) print (solution_string) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 虽然现在的Angr支持函数scanf了,但之前是不支持的,这道题目是想教会读者,可以在任意地址设置状态,并符号执行。
在任意地址创建状态。
1 project.factory.blank_state(addr=start_address)
创建符号向量,例如,一个代表32位数值的符号。
1 claripy.BVS('name', bit_length)
将符号值赋给寄存器。
1 2 state.regs.REG_NAME = symbolic_value # 例如: initial_state.regs.eax = password0
获取符号变量的一个具体满足约束的值。
1 state.solver.eval(symbolic_value)
04_angr_symbolic_stack 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) start_address = 0x80486ae initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) initial_state.regs.ebp = initial_state.regs.esp password0 = claripy.BVS('password0' , 32 ) password1 = claripy.BVS('password1' , 32 ) padding_length_in_bytes = 8 initial_state.regs.esp -= padding_length_in_bytes initial_state.stack_push(password0) initial_state.stack_push(password1) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval (password0) solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval (password1) solution_string = ' ' .join(map (str , [solution0, solution1])) print (solution_string) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 类似于Level3,但这次scanf读取的值可能直接存储于栈上的局部变量,而非像Level3一样,将值直接传递给3个寄存器。
获得初始状态,angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY和SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS用于设置未初始化的内存、寄存器为符号。
1 2 3 4 5 initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} )
模拟栈帧的建立,令ebp指向当前esp。
1 initial_state.regs.ebp = initial_state.regs.esp
创建2个32位的符号整数。
1 2 password0 = claripy.BVS('password0', 32) # 第一个32位符号整数 password1 = claripy.BVS('password1', 32) # 第二个32位符号整数
根据反汇编,scanf的参数是 ebp-0xc 和 ebp-0x10,相当于:
1 scanf(format_string, ebp - 0xc, ebp - 0x10)
esp开辟8个字节的栈帧。
1 2 padding_length_in_bytes = 8 # 这个值需要根据具体情况调整 initial_state.regs.esp -= padding_length_in_bytes
压栈。
1 2 initial_state.stack_push(password0) initial_state.stack_push(password1)
创建模拟器。
1 simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state)
解析成功状态时,符号的值。
1 2 solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval(password0) solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval(password1)
为什么这里需要设置ebp = esp,并且esp -= 8?
观察反汇编代码,发现之后调用参数的时候,都是基于ebp来调用的,因此这里ebp先设置为esp,然后让esp -= 8,之后压栈操作又会令esp - 4,这个时候,ebp + var_10和ebp + var_C可以正确访问到栈上的符号变量了。
05_angr_symbolic_memory 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) start_address = 0x8048618 initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) password0 = claripy.BVS('password0' , 8 *8 ) password1 = claripy.BVS('password1' , 8 *8 ) password2 = claripy.BVS('password2' , 8 *8 ) password3 = claripy.BVS('password3' , 8 *8 ) password0_address = 0xab232c0 initial_state.memory.store(password0_address, password0) password1_address = 0xab232c8 initial_state.memory.store(password1_address, password1) password2_address = 0xab232d0 initial_state.memory.store(password2_address, password2) password3_address = 0xab232d8 initial_state.memory.store(password3_address, password3) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval (password0, cast_to=bytes ).decode() solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval (password1, cast_to=bytes ).decode() solution2 = solution_state.solver.eval (password2, cast_to=bytes ).decode() solution3 = solution_state.solver.eval (password3, cast_to=bytes ).decode() solution_string = ' ' .join([solution0, solution1, solution2, solution3]) print (solution_string) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 scanf可以获得输入,这个输入在Level3中写入了寄存器,在Level4中写入了栈,在本次案例中,写入了全局变量。
创建起始状态。
1 2 3 4 5 initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} )
创建符号变量。
1 2 3 4 5 # 创建符号字符串,每个8字节 (8*8=64位) password0 = claripy.BVS('password0', 8*8) password1 = claripy.BVS('password1', 8*8) password2 = claripy.BVS('password2', 8*8) password3 = claripy.BVS('password3', 8*8)
使用initial_state.memory.store,将符号值存储到已知的全局变量地址。(偏移地址)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 # 将符号字符串存储到它们在内存中的地址 # 这些地址需要通过反汇编确定 password0_address = 0xab232c0 # 示例地址 initial_state.memory.store(password0_address, password0) # 默认字节序,对于字符串通常OK password1_address = 0xab232c8 # 示例地址 initial_state.memory.store(password1_address, password1) password2_address = 0xab232d0 # 示例地址 initial_state.memory.store(password2_address, password2) password3_address = 0xab232d8 # 示例地址 initial_state.memory.store(password3_address, password3)
解析符号的值。
1 solution_state.solver.eval(symbolic_value, cast_to=bytes).decode()
06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) start_address = 0x80486af initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) password0 = claripy.BVS('password0' , 8 *8 ) password1 = claripy.BVS('password1' , 8 *8 ) fake_heap_address0 = 0x4444444 pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0 = 0xa2def74 initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0, fake_heap_address0, endness=project.arch.memory_endness, size=4 ) fake_heap_address1 = 0x4444454 pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1 = 0xa2def7c initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1, fake_heap_address1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness, size=4 ) initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address0, password0) initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address1, password1) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval (password0, cast_to=bytes ).decode() solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval (password1, cast_to=bytes ).decode() solution_string = ' ' .join([solution0, solution1]) print (solution_string) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 本次案例中,输入的值保存到了堆上。
在scanf之后的地址创建初始状态。
1 2 3 4 5 6 start_address = 0x80486af # scanf 之后 (示例) initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} )
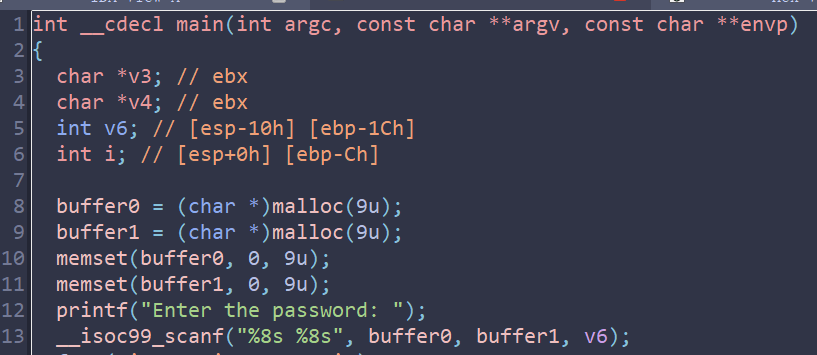
程序中会有一个指针变量(全局变量或是局部变量)用于存储malloc返回的地址,如上图的buffer0、buffer1。
选择一个angr知道的、未被使用的“伪造堆地址”,使用下面这个语句修改存储malloc结果的指针,让它指向伪造的堆地址,这里的endness指字节序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 # 伪造的堆地址,我们可以控制这块内存 fake_heap_address0 = 0x4444444 # 存储了 malloc返回地址 的那个指针变量的地址 (需反汇编确定) pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0 = 0xa2def74 # 示例 initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1, fake_heap_address1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness, size=4)
在对地址上存储符号向量。
1 2 3 4 5 password0 = claripy.BVS('password0', 8*8) password1 = claripy.BVS('password1', 8*8) # 在伪造的堆地址上存储我们的符号密码 initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address0, password0) initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address1, password1)
探索路径。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 def is_successful(state): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort(state): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort)
解析符号。
1 2 solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval(password0, cast_to=bytes).decode() solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval(password1, cast_to=bytes).decode()
07_angr_syombolic_file 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) start_address = 0x80488bc initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) filename = 'FOQVSBZB.txt' symbolic_file_size_bytes = 8 password_data = claripy.BVS('password_file_content' , symbolic_file_size_bytes * 8 ) password_file = angr.storage.SimFile(filename, content=password_data) initial_state.fs.insert(filename, password_file) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] solution_bytes = solution_state.solver.eval (password_data, cast_to=bytes ) print (solution_bytes.decode()) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 程序会从文件中读取密码,而不是标准的输入或命令行参数。
解题思路:
确定程序读取的文件名和预期的大小。
1 2 filename = 'FOQVSBZB.txt' # 程序将要读取的文件名 (示例) symbolic_file_size_bytes = 8 # 假设密码是8字节
创建符号位向量代表文件内容。
1 2 # 创建代表文件内容的符号位向量 password_data = claripy.BVS('password_file_content', symbolic_file_size_bytes * 8)
使用angr.storage.SimFile(filename, content=symbolic_data)创建一个模拟文件,内容是我们的符号数据。将这个模拟文件插入到初始状态的文件系统中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # 创建一个模拟文件,其内容是我们的符号数据 # 'r'表示只读模式,Angr的SimFile也接受模式参数,但content更直接 password_file = angr.storage.SimFile(filename, content=password_data) # 将这个模拟文件插入到初始状态的文件系统中 # 当程序尝试打开并读取 'FOQVSBZB.txt' 时,它会读到 password_data initial_state.fs.insert(filename, password_file)
当程序执行 fopen, fread 等文件操作时,它会从我们提供的这个符号化文件中读取。
08_angr_constrains 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) start_address = 0x804863c initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) password_size_bytes = 16 password = claripy.BVS('password' , password_size_bytes * 8 ) password_address = 0x804a040 initial_state.memory.store(password_address, password) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) address_to_check_constraint = 0x8048683 simulation.explore(find=address_to_check_constraint) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] constrained_parameter_address = 0x804a040 constrained_parameter_size_bytes = 16 constrained_parameter_bitvector = solution_state.memory.load( constrained_parameter_address, constrained_parameter_size_bytes ) constrained_parameter_desired_value = 'OSIWHBXIFOQVSBZB' .encode() solution_state.add_constraints(constrained_parameter_bitvector == constrained_parameter_desired_value) solution_bytes = solution_state.solver.eval (password, cast_to=bytes ) print (solution_bytes.decode()) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
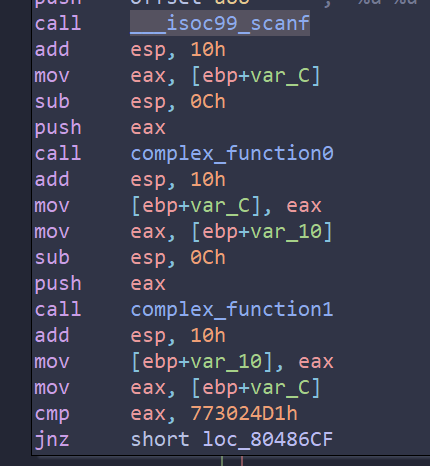
解析 程序中有一个非常复杂的检查函数(check_equals_...),它逐字节比较输入经过某个 complex_function 转换后的结果与一个硬编码的字符串。如果让Angr完整符号执行这个检查函数,由于大量的分支 (每个字节比较都是一个分支),会导致状态爆炸,非常耗时。
创建初始状态,假设这里的0x804863C是符号执行的起始地址。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 start_address = 0x804863c initial_state = project.factory.blank_state( addr=start_address, add_options={ angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS } )
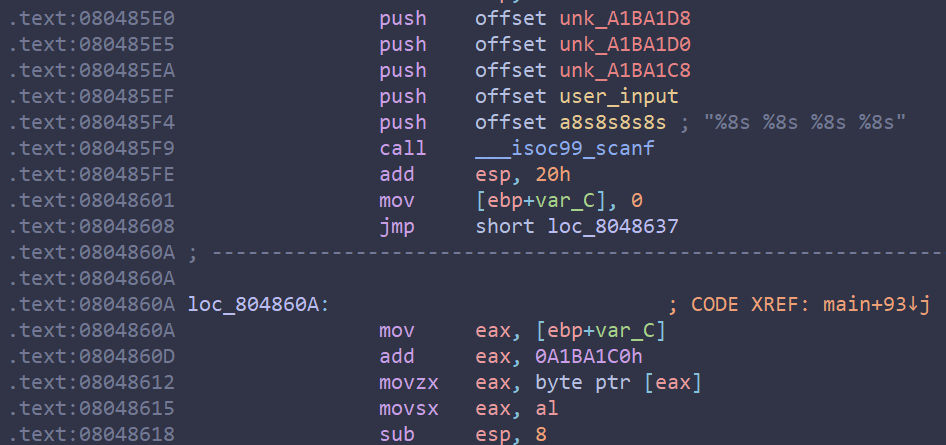
符号化密码,假设密码是16字节长,创建一个16字节的符号变量,password_address是原始密码的内存地址,
1 2 3 4 password_size_bytes = 16 password = claripy.BVS('password', password_size_bytes * 8) password_address = 0x804a040 initial_state.memory.store(password_address, password) # 将符号变量password写入内存地址0x804a040
创建模拟管理器,探索目标地址。
1 2 3 4 simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) address_to_check_constraint = 0x8048683 simulation.explore(find=address_to_check_constraint)
处理成功状态。
1 2 if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0]
加载和约束输出。solution_state.add_constraints(…)添加约束。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 constrained_parameter_address = 0x804a040 constrained_parameter_size_bytes = 16 constrained_parameter_bitvector = solution_state.memory.load( constrained_parameter_address, constrained_parameter_size_bytes ) constrained_parameter_desired_value = 'OSIWHBXIFOQVSBZB'.encode() solution_state.add_constraints(constrained_parameter_bitvector == constrained_parameter_desired_value)
求解密码。
1 2 solution_bytes = solution_state.solver.eval(password, cast_to=bytes) print(solution_bytes.decode())
09_angr_hooks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ): path_to_binary = argv[1 ] project = angr.Project(path_to_binary) initial_state = project.factory.entry_state( add_options = { angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY, angr.options.SYMBOL_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) check_equals_called_address = 0x80486ca instruction_to_skip_length = 5 @project.hook(check_equals_called_address, length=instruction_to_skip_length ) def skip_check_equals_ (state ): user_input_buffer_address = 0x804a044 user_input_buffer_length = 16 user_input_string_bv = state.memory.load( user_input_buffer_address, user_input_buffer_length ) check_against_string_concrete = 'OSIWHBXIFOQVSBZB' .encode() return_value = claripy.If( user_input_string_bv == check_against_string_concrete, claripy.BVV(1 , 32 ), claripy.BVV(0 , 32 ) ) state.regs.eax = return_value simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Good Job.' in stdout_output def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) return b'Try again.' in stdout_output simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()).decode()) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main(sys.argv)
解析 设置钩子。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 check_equals_called_address = 0x80486ca instruction_to_skip_length = 5 @project.hook(check_equals_called_address, length=instruction_to_skip_length ) def skip_check_equals_ (state ): user_input_buffer_address = 0x804a044 user_input_buffer_length = 16 user_input_string_bv = state.memory.load( user_input_buffer_address, user_input_buffer_length ) check_against_string_concrete = 'OSIWHBXIFOQVSBZB' .encode() return_value = claripy.If( user_input_string_bv == check_against_string_concrete, claripy.BVV(1 , 32 ), claripy.BVV(0 , 32 ) ) state.regs.eax = return_value
加载二进制文件 :创建 angr 项目,解析程序。
设置初始状态 :从程序入口(main)开始,允许 angr 模拟 scanf 和 complex_function。
钩子处理 :
在 check_equals_ 调用处(0x80486ca)设置钩子,跳过其执行。
模拟 check_equals_ 的行为,比较 0x804a044 处的符号输出与目标字符串,设置 eax 为 1(匹配)或 0(不匹配)。
符号执行 :
探索所有路径,寻找输出 “Good Job.” 的状态,避免输出 “Try again.” 的状态。
提取输入 :从成功状态的 stdin 中提取输入密码,打印结果。
利用angr解混淆 已经有大佬写过了,利用angr符号执行去除虚假控制流,思路很简单,不是活跃状态的基本块全部NOP掉。
思路:https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-266005.htm
项目代码:https://github.com/bluesadi/debogus
局限也是有的:
依赖于z3约束求解,如果解不出来,则判定为非活跃状态的基本块;
未约束导致路径爆炸。
我的理解 什么是状态、成功状态? 在一开始,符号执行还没开始的时候,需要一个初始状态(寄存器、堆栈、内存等,它们可以被定义成符号),初始状态没有对符号的约束;
而成功状态就是走到了目标地址或者目标行为的状态,此时的寄存器、堆栈、内存等共同构成了成功状态;
在初始状态到成功状态的过程中,angr会为被定义为符号的变量收集约束,正是有了这些约束,程序才可以从初始状态走到成功状态 ;
在成功状态时,可以调用angr相关的函数,根据约束计算出符号变量的值。
状态的更新与分裂? 每个基本块都有一个状态,每执行一条指令,状态都会对自身进行更新 ;而当来到条件分支的时候,会基于当前的状态,创建分裂 出独立的、并行的多个状态,此时称作产生 了新的状态。
angr符号执行与基本块的关系? 基本块 的特点是:
只有一个入口点(第一条指令);
只有一个出口点(最后一条指令,通常是跳转、返回、条件分支)。
angr 是一种符号执行框架,它通过将程序的输入(例如标准输入或参数)表示为符号变量(claripy.BVS),模拟程序的所有可能执行路径。angr 跟踪符号变量如何影响程序的状态(寄存器、内存等),并使用约束求解器(通常是 Z3)来确定哪些输入能够引导程序到达特定目标(如某个地址)。
在 angr 的符号执行过程中,基本块是程序执行的“原子单位”,而符号执行是基于这些基本块进行路径探索的。
基本块是执行的单位
angr 在符号执行时,会将程序分解为基本块(通过静态分析生成 CFG 或动态执行时解析)。每个基本块代表一段连续的指令,angr 会逐块模拟执行。
在执行一个基本块时,angr 更新当前状态的寄存器、内存等内容,并根据基本块的出口指令(例如跳转、条件分支、返回)决定下一步的执行路径。
状态分叉与基本块的出口
符号执行跟踪基本块的路径
angr 的符号执行本质上是沿着 CFG 的路径探索,每个路径由一系列基本块组成。angr 维护一个状态池(通过 SimulationManager,即 simgr),跟踪每个状态对应的执行路径。
每个状态在执行一个基本块后,会更新其上下文(例如寄存器、内存),并根据基本块的出口指令跳转到下一个基本块。
约束累积与基本块
在执行基本块的过程中,angr 会根据指令的逻辑为符号变量添加约束。例如,如果一个基本块包含比较指令 cmp input[0], ‘A’,angr 会在分支时为符号变量 input[0] 添加约束(如 input[0] == ‘A’ 或 input[0] != ‘A’)。
这些约束是符号执行的核心,用于在成功状态中求解具体输入。
成功状态与基本块
当 angr 的符号执行到达目标地址(例如 find=print_good_address),对应的状态通常位于某个基本块的入口或内部。成功状态包含了从初始状态到目标地址的完整执行路径(即一系列基本块),以及符号输入的约束集合。
通过 solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()),angr 求解这些约束,得到引导程序到达目标基本块的输入值。
同时,angr 不会为每条指令生成新状态(而是基于原状态进行更新),而在基本块的边界(特别是条件分支)生成新状态 。状态分叉发生在基本块的出口,基于分支条件。